Welcome to the basil forest!
It’s official- harvesting plant medicine has begun in earnest and, depending on who’s in your garden, won’t stop until first frost. This time of year it’s all about the Aster and Mint families.
Blossoms like calendula, chamomile, echinacea and yarrow all benefit from regular deadheading, and create small consistent harvests that lend themselves well to infusions in oil or apple cider vinegar to create soothing topical applications for all manner of skin ailments. Infuse a pint of oil (local sunflower, olive or jojoba are lovely) with freshly-wilted chamomile, calendula and yarrow, then blend with local beeswax for tins of salve. You’ll be the hero of every chapped lip and dry hand you know!
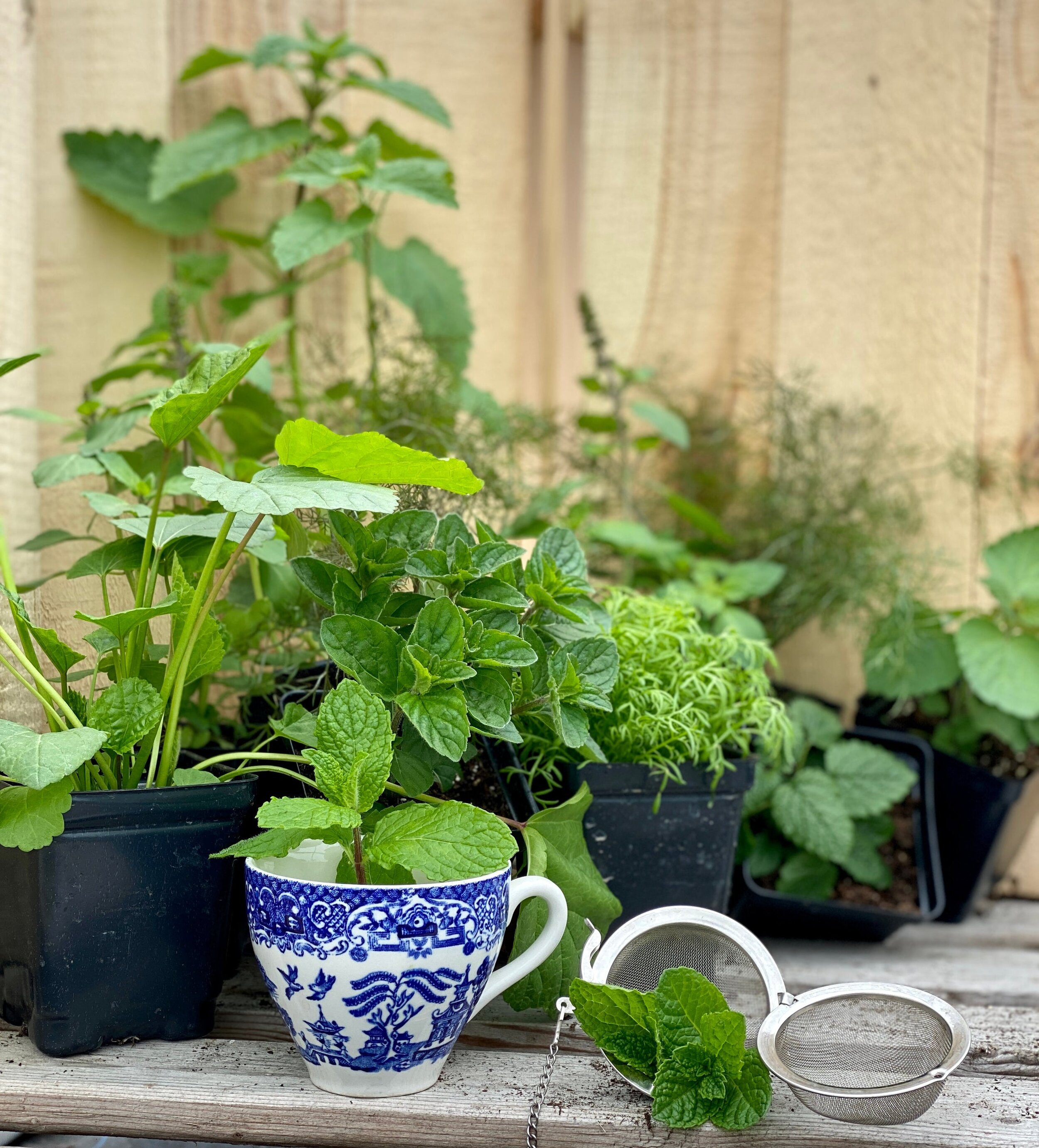
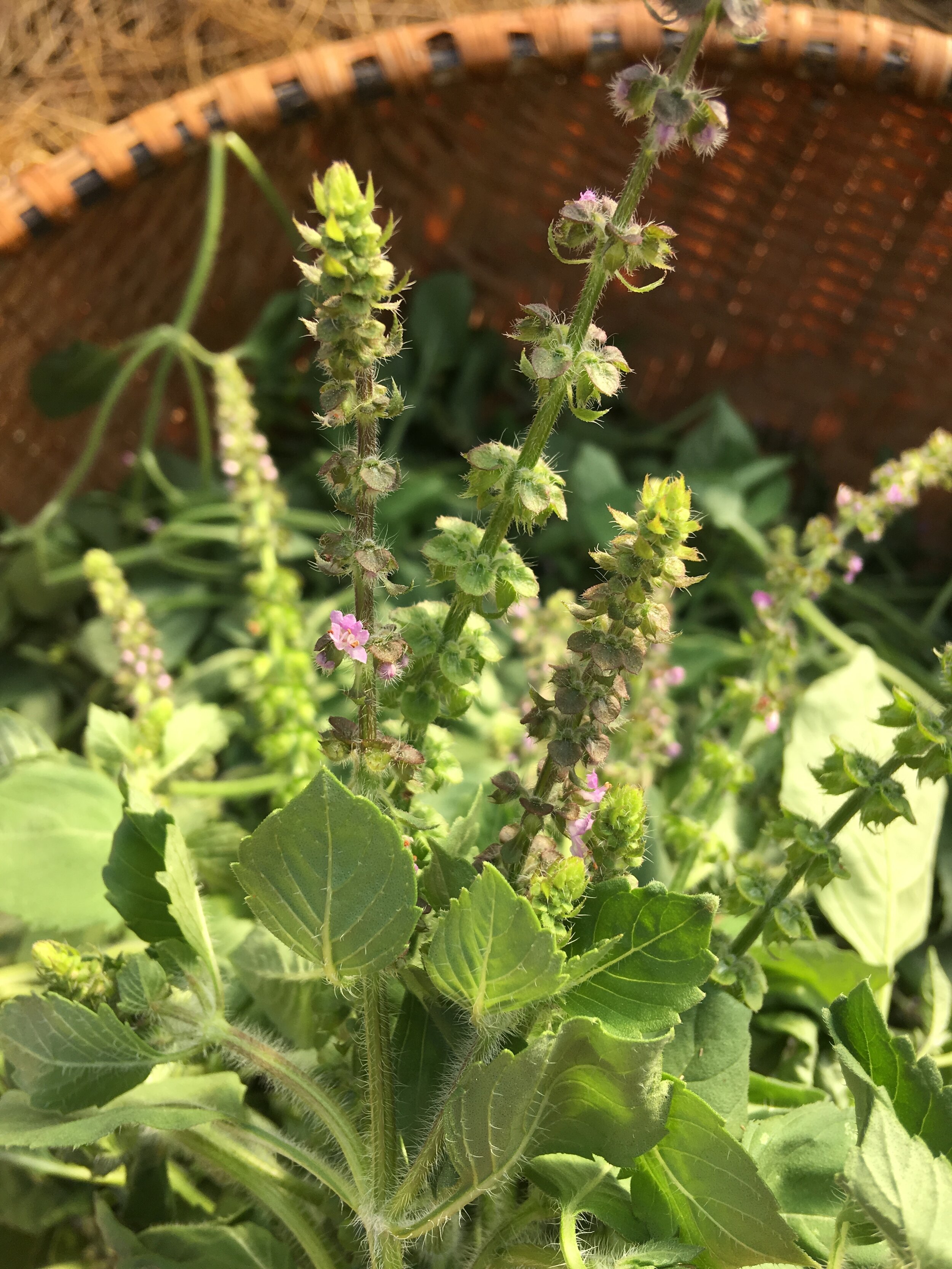
Mint family plants like lemon balm, tulsi, basil, peppermint and spearmint should be harvested when the bottommost flowers on their spikes have begun blooming, or slightly before. Cutting at this time encourages bushy regrowth, and gives you the highest quantity of aromatic leaves and flowers without a lot of stem or seed. Be sure to make yourself a half gallon of fresh mint tea to have on hand in the fridge- plants with high volatile oil content (read: nice and smelly) will last the longest in the fridge, as the volatile oils do double duty inhibiting fermentation. This also clues us in to their amazing ability as general support for our immune system. Harvest on a hot, sunny day and dry quickly in a breezy, warm spot to get the highest volatile oil content from your plants.
Tulsi drying on racks in our greenhouse
We are doing a big sale this week- buy one herb pot, get one free! Culinary staples, perennials, and tea herbs are all available and will continue to produce well into early fall. Come by the greenhouses between 8-6 every day to stock up on herbaceous joy this week!
This is a great time to bulk up your herb garden with a new-to-you plant or more of your favorites. Include a couple of lemon verbena and rosemary plants to make Sophie’s favorite “lazy tea”: Just add a few whole leaves of lemon verbena and a sprig of rosemary to the bottom of your cup, then cover with hot water and steep five minutes. It’s the perfect afternoon pick-me-up, and is even better when steeped overnight and served on ice.
No more room for herbs in the garden? We’ve got you covered! We are now offering bulk fresh herbs for pickup at our greenhouse. Dry sage and thyme for holiday gifts, brew tulsi and anise hyssop tea for your whole cookout, make a cool mint bath for your sunburn… the possibilities are endless!
Building mesh screens to sift dried herbs
We have some upcoming classes for the herbal enthusiast (registration required):
July 20th: Know and Grow your Chicory. Julie and I are teaming up to talk all things chicory- from its use as an ancient medicinal herb, to coffee substitute, to revered Italian vegetable and everything in between. Taste tests included!
August 5th: First Thursdays in the Garden: Chad will be talking integrated pest management this month- how we do it at RWP and how you can at home. Julie will offer a behind-the-scenes tour of our greenhouses. I’ll also be hosting our September 2nd edition to talk about fall herbs!
August 21st: Harvesting and Processing Medicinal Herbs. We’ll dive deep into the different ways to preserve and use the herbal bounty in this hands-on three-hour class, so bring your questions and jars!
Let us know what you’re making from the season’s bounty, and of course come by any day 8-6 with questions, concerns, and success stories. We’re happy to help and love hearing about your garden journeys.