In our attempt to reduce plastic, we have been growing a few plants in fiber pots. They are not perfect, but they have been good for a few things. One of our experiments was with native perennials. We wanted to give you an option that feels ecological for those extra-eco plantings, so this week’s Plant(s) of the Week are a trio of power house perennials for the native / pollinator garden:
Asclepias tuberosa, a.k.a. Butterfly Weed - a little slow to get established, but once it takes off, it provides a bright pop of orange all summer long.
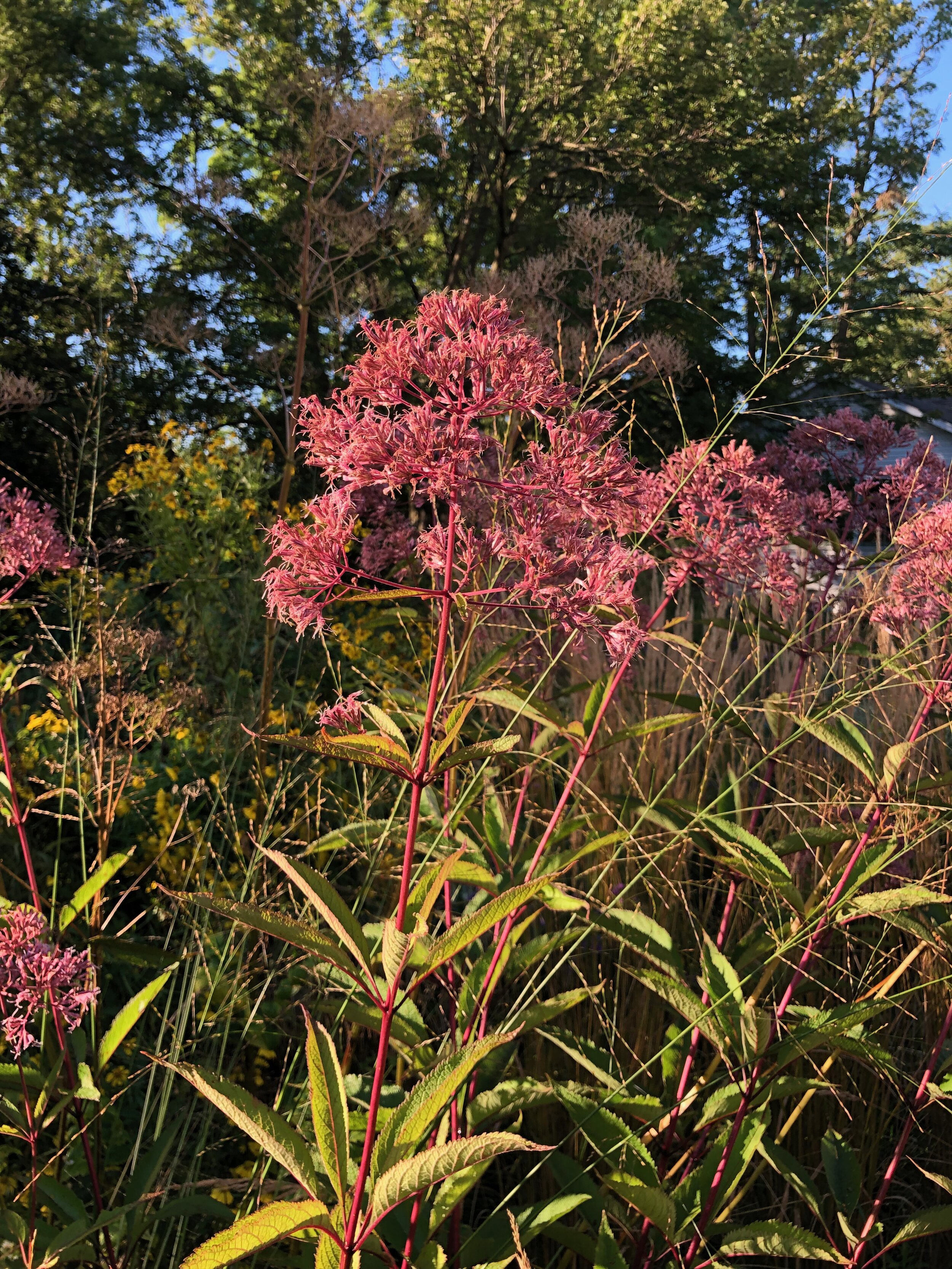
Eupatorium maculatum, a.k.a. Joe Pye Weed - a tall meadow plant that looks so striking in the landscape and is always covered in bees and butterflies
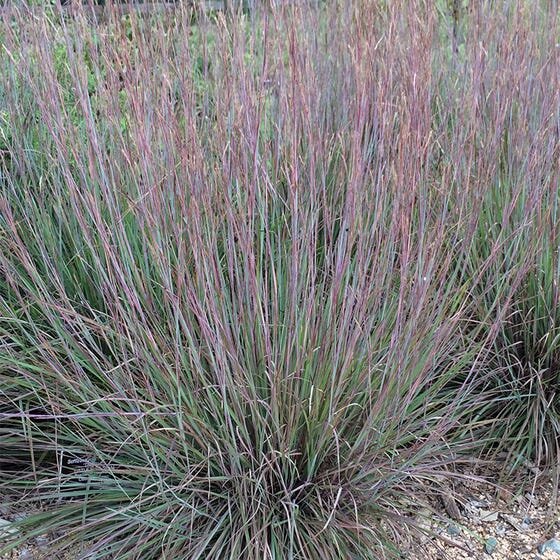
Schizachrium scoparum, a.k.a. Little Bluestem - the Audubon calls this a living bird feeder.
You can buy one ($5.99), get one free of any of the plants in this power trio. It is okay to mix and match, and we encourage you to bring home all three so that you can create a little pollinator habitat with three plants that bloom at different times, at three different heights, and create a perfect little haven for our smallest friends.
In addition, we have lots of great perennials in smaller sizes this year so that you can add to your existing garden or create a new flower bed without breaking the bank. Quarts are $9.99, 4” pots are $4.99.
We have the following in smaller sizes:
Eupatorium perfoliatum, a.k.a. Boneset
Saponaria ocymoides, a.k.a. Rock Soapwort
Heuchera a.k.a. Coral Bells in lots of different varieties
Rudbeckia hirta ‘Indian Summer’, ‘Goldilocks’, and ‘Cherokee Sunset’
Allium cernuum, a.k.a. Nodding Onion
Centranthus ruber a.k.a. Rosy Red Valerian or Jupiter’s Beard
Chasmanthium latifolium, a.k.a. Northern Sea Oats
Hibiscus moscheutos, a.k.a. Hardy hisbiscus ‘Luna Swirl’
Dianthus - lots of varieties
Monarda bradburiana - a favorite native plant of mine. It makes a great ground cover and grows well in all sorts of conditions
Monarda didyma, a.k.a. Scarlet Beebalm
Eryngium yuccifolium - another favorite native plant of mine. It’s got great architecture in the summer garden.
Echinacea purpurea ‘White Swan’
Achillea millefolium ‘Moonshine’ and ‘Sassy Summer Sangria’
Nepeta x faassenii ‘Junior Walker’
Heliopsis helianthiodes ‘Summer Night’ - this won’t stay at this size / price point for long. It is a fast growing, big plant, and will get bumped up to a gallon or two gallon pot soon. It is a great filler for the back of the border where you want late July (yellow) color and height. It would look great with this week’s power trio Plant(s) of the Week!
In the Garden
It is time to harvest garlic. While the rains have made it hard to find a good time to pick, we want to encourage you to do it sooner rather than later. The longer the garlic sits in wet soil, the less success you will have to cure it properly. Harvest now so that the skins don’t rot and leave all the cloves exposed all winter long. To learn more about harvesting and curing garlic, you can read these blog posts from the way back machine.
Now is a great time to assess the perennial gardens and take notes about changes you would like to make. It is often a time of year with less color in the garden. The early bloomers are done, and the late season flowers haven’t started quite yet. Some great additions: salvias, echinacea, flowering shrubs such as smooth leaf hydrangea, Russian sage, geranium, Eryngium, and lots more. We can help you out with your selection if you tell us what you are looking for in terms of height, color and exposure.
I am ripping out the old peas and planting more greens of all sorts. I have been harvesting lettuce, beets, kohlrabi, cucumbers, greens of all sorts, and radicchios of all sorts. Take a look at anything that is sub-par in the garden, and turn that space into something productive. We have lots of new 4-pack veggies each week and can help you make the most of the summer and fall with succession plantings that you will harvest until the ground freezes.
I have to admit that there is a pile of bark mulch in my driveway that doesn’t seem to magically go away. I bought it to add to my arsenal of murder weapons in my attempt to eradicate the Bishop’s Weed at our house. But it is still there, and so is the Bishop’s Weed. Do you have any projects that you can never make time for? We all do, right? I am hoping to wrap up some of those danglers this week. And no, I don’t think bark mulch will really help to kill the Bishop’s Weed. But it will hide the ugly black plastic that I will smother it with first. Wish me luck.
Happy gardening,
Julie