Planting garlic in Vermont is a great way to extend the gardening season and gives you a crop that is perfect in so many dishes, stores well all winter long and even generates its own seed. It is a perfect way to tune into the cycles of the gardening season and feel like you are growing an important part of your diet. Garlic is expensive to purchase so there are savings to be had with your own garlic crop. Please follow this guide for easy, step-by-step instructions that will give you a garlic patch for life. I have been growing out my own garlic for 18 years and usually do not need to ever buy seed stock or garlic in the grocery store. The pleasures of garlic growing are abundant and I encourage you to get familiar with this wonderful and simple crop.
When to start the cycle?
Planting dates in Vermont are anytime between mid October and late October. It is best to wait until then, because if you plant too early, the bulbs will break out of dormancy too soon and this weakens the plant going into our harsh winters. If you plant the cloves during those last two weeks of October, it gives them just the right amount of time to take root and hunker down until spring, but not send out any top growth.
To plant garlic, you need to follow a few easy steps.
1. Bed preparation.
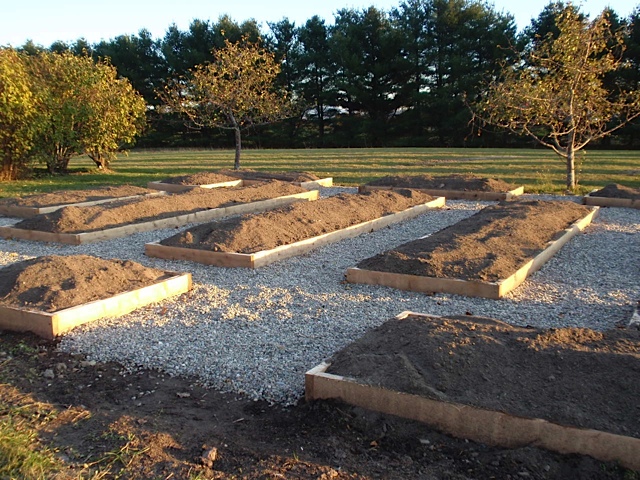
This is the act of making your garden soil ready for garlic planting. You want a nice patch of garden, that is worked deeply so that the soil is loose about a foot down in depth. If your garden is very compacted and hard, the garlic will not be able to grow well and you will be sure to end up with small heads of garlic that are tedious to peel and not all that satisfying. You can prepare the bed with a 3 prong fork by digging in straight down, tilting the handle of the fork back and forth, and loosening the hard pan. This is a good work out! Don’t hesitate to get dirty here by kneeling in the earth and breaking up the clods of soil with your hands so they are not chunky at all. Add a bit of well rotted manure or compost at this time. Not too much. For a 5 by 10 bed, maybe a 5 gallon bucket’s worth. You don’t want to over feed the garlic roots in the fall, but a little compost will add organic matter and that will help the structure of the soil, keeping it loose, able to retain some moisture without staying too wet.
Take your time and your garden will reward you. I always look at garlic planting as a soulful moment in the gardening cycle. It is saying goodbye to summer and embracing the dormancy of winter, when seeds deep below the surface slowly get ready for their spring emergence. Living in a climate with such long winters, I need these small, but important, rituals to remind me that spring will come and the cold barren winter is a necessary part of it all. The seed garlic is planted in the fall because it needs to send roots far into the earth in order to feed itself the following year. I take this as a metaphor for my own winter activities that feed me all year long - catching up on sleep, feeding my mind with more reading time, eating great, nourishing foods, and spending more time with friends and family. I digress here, but these are the thoughts I have as I plant garlic, and after many years of doing it, I find that it is a necessary part of my mental preparation for winter.
2. Mark the rows with a hoe, or hand tool. I usually keep the rows about 12 inches apart and since my beds are about 4 feet wide, I keep 3 rows per bed and can easily reach the center. Just drag your tool - the sharp tip of a hoe or the narrow edge of a hard rake works well - through the soil to delineate the rows. You can use string and stakes if it is important to be straight, but I don’t bother with that at all.
3. Break up the garlic heads into individual cloves. Do not peel! And notice that one end is the root end and one end is the stem end. This will be important for planting right side up with the root end pointing straight down and the stem end pointing straight up.
4. Space out the cloves. Lay the cloves on the top of the soil, following the line you have just drawn in the soil. Allow about 6 inches between all the cloves.
5. Planting, spacing, and yields
Now you can start to plant. I always kneel down and take my time to feel the earth under me at this point. It just feels good and is a way to say goodbye to the garden before winter! Then, take a bulb planting tool, or a sturdy, sharp pointed stick, or your hand if your soil is soft and pliable, and poke a hole about 4 to 6 inches down. Shove the clove of garlic deep down, root end down, and cover up with the soil. Continue down the row and repeat until all is planted. Three heads of garlic will turn into about 24 heads next spring - assuming your garlic has about 8 cloves per head. . And with 6” by 12” spacing, a 5’ x 10’ patch of garlic will yield about 60 heads of garlic. That is enough to enjoy one head of garlic per week, all year long, and still have some left over for planting. To plant a patch this big, you will need to plant the equivalent of 7 to 10 heads of garlic.
6. Compost and mulch.
I usually add another 4” of compost or well rotted horse manure to the bed. I then leave it like that for about 6 weeks. Then in mid to late December, I cover the bed with a thick layer of straw. You can also use leaves here, but straw is the best insulator with hollow stems that trap air and keep everybody warm down below. Another advantage of straw is that it usually does not have weed seeds in it; mulch hay, straw’s poor cousin, should be avoided since it is laden with all sorts of perennial grass and weed seeds. The straw moderates the winter soil temperature and prevents buckling and heaving which could push those garlic cloves up and out of the ground.
Let winter pass you by now, and next......
7. Spring time chores with garlic.
Once the snow melts and the soil warms up a bit, your garlic will break dormancy and magically pop up out of the earth. It is important to pull back the straw to let the garlic see sunlight. If you wait a bit too long, and pull back the straw only to see a bunch of yellowing stems, don’t worry! The garlic shoots will green up in no time and will look fabulously sturdy after a week or so of direct sunlight. I usually pull the straw into the garden path, let it pile up there and then replace it around the growing garlic to block out weeds once the garlic plants are about 8 inches high. I often will add a little granular fertilizer at this time, before putting the mulch back in place. For a 5 by 10 garlic patch about 3 cups of Pro-Gro from North Country organics or one bag of Compost Plus from Vermont Compost Company is just about right. This will insure you get large, easy to peel cloves that taste great.
8. Garlic scapes will appear on stiff neck garlic around late May. These look like green curly cues with a pointy end that gracefully swoops down and around, waving in the breeze. This is the budding and flowering portion of the garlic plant. It should be removed to help the plant spend its energy on sizing up the goods below ground. If it is allowed to flower, the plants’ strength will go towards the flower and the garlic forming below ground will be the weaker for it. The good news here is that the “scapes” as they are called, are good to eat. I usually cut off the pointy tip - it is rubbery and inedible, and then slice up the round stem and use it in stir fries, stews, pasta dishes, or pickles. When cooked, it has the texture of a nice green bean and the flavor of mild garlic. It is absolutely delicious and a once a year treat that marks the beginning of summer - a harbinger of good things to come.
9. When to harvest?
Garlic is ready to harvest when about 70% of its leaves have turned yellow. This is somewhat subjective, and should be taken as not a hard and fast rule, but rather a guide. You can dig up one head of garlic and look for signs of well formed skin, plump cloves, and individuation (cloves that are individually formed, and not one big mass). This is usually some time in late July. In very wet and rainy years, sometimes it makes more sense to take the garlic our of the ground a little early so that the skin does not rot in the damp earth.
10. How to harvest?
Take out your three prong fork again and use it to loosen the soil around the outside edges of each garlic row. This will break up the soil enough to allow you to pull out each plant with a firm yank. (If the stems break off, it is likely you waited too long and the skin and stems are starting to rot. At that point, just dig up the cloves with a spade and they will be okay in taste; they just won’t store well. ) Lay the plants on the surface of the soil so that they start to dry off. Once all the garlic is pulled up, wipe it with a towel or rag, and get ready to tie it into bundles. I usually take about 8 plants, hold them together in one hand, and with the other hand, wrap twine around the whole bundle. Tie off the twine and then hang the bundle in a dark airy space. The rafters of a garage, shed or barn work well. If you don’t have that type of space, just find a place out of the rain, out of direct sunlight and with good air circulation - a covered porch? a dry basement with a fan running? a spare bedroom that can get a little dirty? (no shag rugs please!).
11. Curing the garlic
Curing is the process of letting the garlic dry which makes the papery skin that allows the garlic to keep all winter. The stems will turn brown and brittle and the exterior of the bulbs will become dry and paper-like, just like garlic in the store. At this point, it is okay to cut off those dry stems, wipe off any remaining dirt, cut off the roots, and place your garlic in a crate to store it. This can be done anytime from 3 to 6 weeks after you initially hang up the garlic to dry.
12. Storing the garlic
Once the garlic is cured, cleaned and trimmed, you are ready to store it for eating all winter long. Garlic is best stored in the dark. In an airy, dry, cool place. I use milk crates, covered with a piece of burlap, and keep the crate in a very cool part of the basement. Ideal garlic storing temperatures are between 35 and 45 degrees, but a refrigerator is too humid, so please don’t be tempted to use that as a storage method. Other good places to store garlic (and onions for that matter) are unheated attics, attached garages that don’t freeze, but are not heated, or 3 season porches that do not freeze. Root cellars are great, but most of us don’t have one. If well stored, garlic will last until April or May - almost right in time for the garlic scape harvest!
13. Finding seed stock.
Until you build up your own supplies, you will have to purchase seed garlic. There are many great resources for garlic and for finding garlic seed, I recommend Johnny’s Selected Seeds, or locally, Last Resort Farm in Monkton, Hudak Farm in Saint Albans, or any farmer at your local farmers market who has nice looking seed stock. Seed stock is basically sorted out of the garlic harvest and selected for the following the following traits:
- good size
- evenly formed cloves
- strong stem
- well formed skin
- great flavor
- ability to store for a long time
If you have been growing out your garlic in your garden, you can pick out the best cloves at cleaning and storing time. Set these aside in a safe place where they will not be eaten and come October, experience the joy of planting your own seed garlic.
14. Plant garlic. Repeat Step 1. above and the cycle starts all over again!